电子商务网站建设与实例心得做生存分析的网站
本文分享10个常用电路,供大家参考学习,需要具体资料可以私聊我。
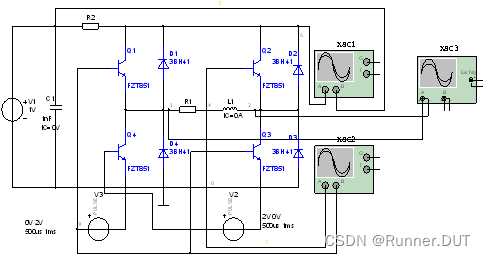
1、基于三极管的DC-AC全桥逆变电路
该电路利用脉冲控制Q1/Q3与Q2/Q4导通从而改变电流流过负载的方向,将直流信号逆变成交流信号。
电路图:
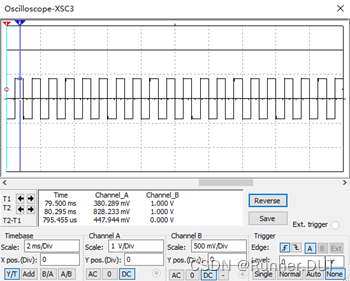
输入输出结果:
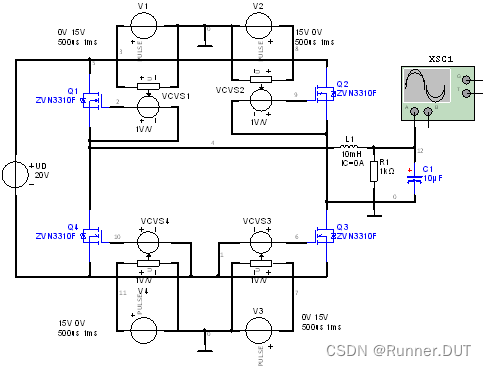
2、基于MOSFET的DC-AC全桥逆变电路
该电路利用电压源线性控制Q1/Q3与Q2/Q4导通从而改变电流流过负载的方向,将直流信号逆变成交流信号。
电路图:
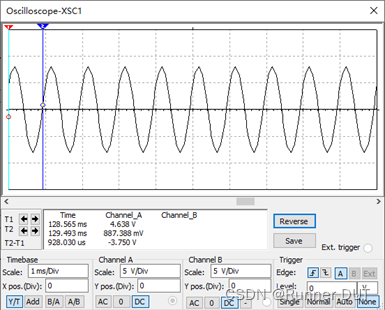
输入输出结果:
3、SVPWM模块电路
该电路通过比较三角波和正弦波大小,控制PWM信号输出。
电路图:
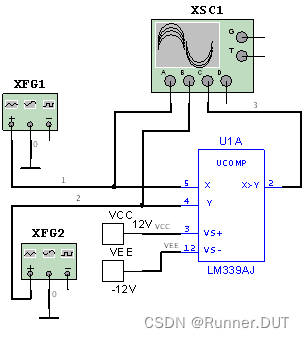
输入输出结果:
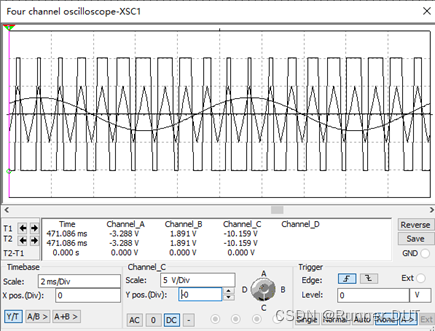
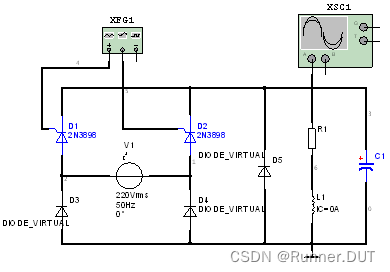
4、单相半控桥式整流电路
该电路通过控制晶闸管导通和关断,交流信号变成直流信号达到整流的目的。
电路图:
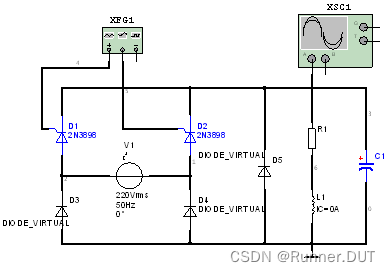
输入输出结果:
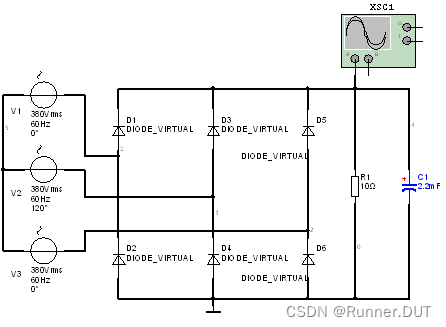
5、三相桥式整流电路
该电路利用二极管直接控制电压的方向。
电路图:
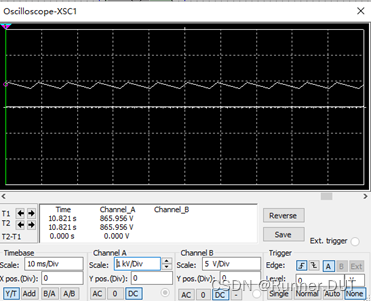
输入输出结果:
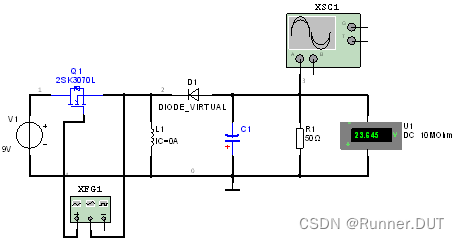
6、直流降压-升压斩波电路
该电路中当MOS管导通,电感储存能量;MOS管关闭,电感释放能量。
电路图:
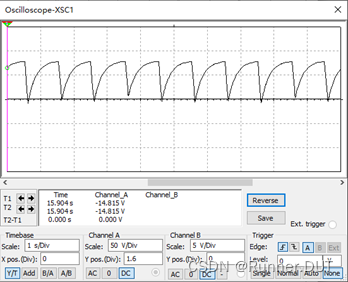
输入输出结果:
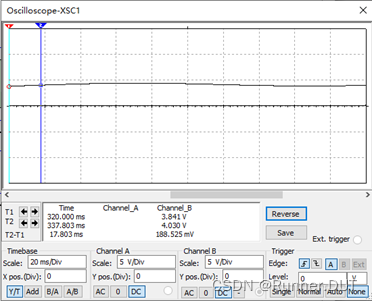
7、直流降压斩波电路
该电路中当MOS管导通,电源向负载供电;MOS管关闭,电感通过二极管小回路释放能量。
输入输出结果:
8、直流升压斩波电路
该电路中当MOS管导通,电感充电,电感两端电压升高;MOS管关闭,电感放电,同时叠加上输入电压。
输入输出结果:

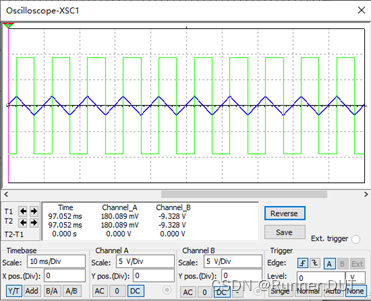
9、三角波发生电路
该电路关键原理在于在方波产生电路的后级增加积分电路实现三角波输出。
输入输出结果:
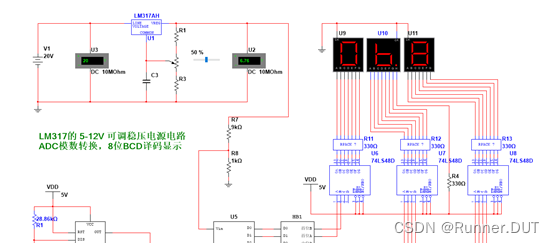
10、8位ADC应用-LM317可调稳压电源加BCD码显示电路
该电路ADC模拟端接稳压电源输出端,ADC输出端经过译码器电路到二极管显示电压值。
本文大部分内容都属于原创,如需转载,请附上本文网站,
如果需要相关的仿真图、程序代码等资料可以直接私信我,我会及时回复。
