app网站开发公司的logo个人网站推广费用
云原生安全作为一种新兴的安全理念,不仅解决云计算普及带来的安全问题,更强调以原生的思维构建云上安全建设、部署与应用,推动安全与云计算深度融合。所以现在云原生安全在云安全领域越来受到重视,云安全厂商在这块的投入也是越来越大。
然而,尽管云原生安全领域取得了显著的发展,但仍然存在一些挑战和问题,德迅云安全在云原生安全方面深耕多年,做云安全出身的它在云原生安全技术方面的研究非常深入,接下来就分享一些关于云原生安全领域的看法和存在的一些挑战和问题,以及对应的安全处理方案。

一、云原生安全领域发展前景
伴随着云计算市场的蓬勃发展,云基础设施投资的快速增长,近年来的云原生安全领域发展势头强劲。随着各行业数智化转型的加速,全社会对云的使用广度和深度大幅提升。根据中研普华研究院的报告显示,超过七成企业计划在未来一年内提升自身云原生环境的安全能力。39.31%的企业已经建设或者将在未来三个月内建设自身的云原生安全能力,同比增长19.5%。这表明企业正逐渐认识到云原生安全的重要性,并付诸实践。
调查数据显示,近三成用户云原生支出占云总体支出超50%。这意味着越来越多的用户将资金投入到云原生建设中,以提升其业务的安全性和效率。
而云原生安全工具和产品的部署也在加速。2023年已有32.77%的用户已经部署并长期维护云原生安全工具或相关产品,44.6%的用户计划未来一年内部署。这显示了市场对云原生安全工具和产品的强烈需求。

1、在海外云安全市场
海外云安全市场正处于快速发展阶段,技术创新活跃,兼并整合频繁。一方面,云安全技术创新活跃,并呈现融合发展趋势。例如,综合型安全公司 PaloAlto 的 Prisma 产品线将 CWPP、CSPM 和 CASB 三个云安全技术产品统一融合,提供综合解决方案及 SASE、容器安全、微隔离等一系列云上安全能力。另一方面,新兴的云安全企业快速发展,同时,传统安全供应商也通过自研+兼并的方式加强云安全布局。
2、在国内云安全市场
市场空间广阔,市场规模上,根据中国信通院数据,2019 年我国云计算整体市场规模达 1334.5亿元,增速 38.6%。预计 2020-2022 年仍将处于快速增长阶段,到 2023 年市场规模将超过 3754.2 亿元。随着国内公有云市场的加速发展,云原生技术的应用也将越来越广泛。
二、云原生安全领域涉及到的一些问题和挑战

问题1:容器安全问题
在云原生应用和服务平台的构建过程中,容器技术凭借高弹性、敏捷的特性,成为云原生应用场景下的重要技术支撑,因而容器安全也是云原生安全的重要基石。
问题2:云原生等保合规问题
等级保护2.0中,针对云计算等新技术、新应用领域的个性安全保护需求提出安全扩展要求,形成新的网络安全等级保护基本要求标准。虽然编写了云计算的安全扩展要求,但是由于编写周期很长,编写时主流还是虚拟化场景,而没有考虑到容器化、微服务、无服务等云原生场景,等级保护2.0中的所有标准不能完全保证适用于目前云原生环境;
通过德迅云安全在云安全领域的研究,对于云计算安全扩展要求中访问控制的控制点,需要检测主机账号安全,设置不同账号对不同容器的访问权限,保证容器在构建、部署、运行时访问控制策略随其迁移;
对于入侵防范制的控制点,需要可视化管理,绘制业务拓扑图,对主机入侵进行全方位的防范,控制业务流量访问,检测恶意代码感染及蔓延的情况;
镜像和快照保护的控制的,需要对镜像和快照进行保护,保障容器镜像的完整性、可用性和保密性,防止敏感信息泄露。
问题3:宿主机安全
容器与宿主机共享操作系统内核,因此宿主机的配置对容器运行的安全有着重要的影响,比如宿主机安装了有漏洞的软件可能会导致任意代码执行风险,端口无限制开放可能会导致任意用户访问的风险。
通过部署主机安全(德迅卫士)及微隔离安全平台,提供主机资产管理、主机安全加固、风险漏洞识别、防范入侵行为、失陷主机网络隔离等功能,对主机进行全方位的安全防护,协助用户及时定位已经失陷的主机,响应已知、未知威胁风险,避免内部大面积主机安全事件的发生。
问题4:安全与合规洞察的缺乏
云环境相比本地环境在安全与合规性方面存在显著的差距。在公有云环境中,用户需要能够查看和控制另一个物理空间的数字资产。随着云原生技术的广泛应用,如无服务器应用等,维护这些数据和访问数据的服务变得日益复杂。因此,如何第一时间自动检测新创建的数字资产并持续跟踪其变更,同时保持适当的上下文以改进风险识别,是云原生安全领域面临的重要挑战。
问题5:多租户环境下的安全隔离
云计算环境是一个多租户环境,不同用户的数据和应用需要得到有效的隔离。如何在容器多变的环境中,确保不同用户之间的数据不会相互干扰,防止数据泄露和滥用,是云原生安全必须解决的问题。
问题6:容器周期及成本问题
容器的生命周期很短,对容器的全生命周期防护时,会对容器构建、部署、运行时进行异常检测和安全防护,随之而来的就是高成本的投入,对成千上万容器中的进程行为进程检测和分析,会消耗宿主机处理器和内存资源,日志传输会占用网络带宽,行为检测会消耗计算资源,当环境中容器数量巨大时,对应的安全运营成本就会急剧增加。
问题7:安全配置和密钥凭证管理问题
安全配置不规范、密钥凭证不理想也是云原生的一大风险点。云原生应用会存在大量与中间件、后端服务的交互,为了简便,很多开发者将访问凭证、密钥文件直接存放在代码中,或者将一些线上资源的访问凭证设置为弱口令,导致攻击者很容易获得访问敏感数据的权限。
三、针对当前的问题和挑战,该如何提升安全防护效果
在了解了上述的关于云原生安全领域存在的挑战和问题,那么该如何在降低安全运营成本的同时,提升安全防护效果呢?
这就需要有“安全左移”概念,“安全左移”就是将软件生命周期从左到右展开,即开发、测试、集成、部署、运行,它的含义就是将安全防护从传统运营转向开发侧,开发侧主要设计开发软件、软件供应链安全和镜像安全。
因此,想要降低云原生场景下的安全运营成本,提升运营效率,那么首先就要考虑到对应的安全方案是否遵循了“安全左移”原则,也就是从运营安全转向开发安全,需要具备能覆盖到从开发安全、镜像安全和配置核查等方面。
1、开发安全
具备能够关注到代码漏洞方面的问题,可以找到因缺少安全意识造成的漏洞和因逻辑问题造成的代码逻辑漏洞。
2、镜像安全
具备能够使用相关工具可对镜像进行持续评估,具有镜像检查能力,可以发现镜像中存在的漏洞。
3、配置核查
具备能够核查包括暴露面、宿主机加固、资产管理等,可以帮助运维和安全人员梳理业务及其复杂的关系,弥补安全与业务的鸿沟。提升攻击者利用漏洞的难度。
上面的的安全要求,为了应对当前云原生领域当前的挑战,德迅云安全云原生安全平台,同时从安全左移和运行时安全两个阶段,在云原生的全生命周期过程中,提供原生的、融合的安全能力。

针对开发安全要求
SCA /SAST
1、SCA可以为开发人员提供了一种自动化且高效的方式来检测和监控开源和第三方组件的使用情况,可以检测开源中的漏洞,评估其安全性和许可证合规性,并降低供应链攻击风险;
2、SAST可以检测内部编写的专有代码中的潜在漏洞,扫描应用程序的代码库以查找潜在漏洞。

针对镜像安全要求
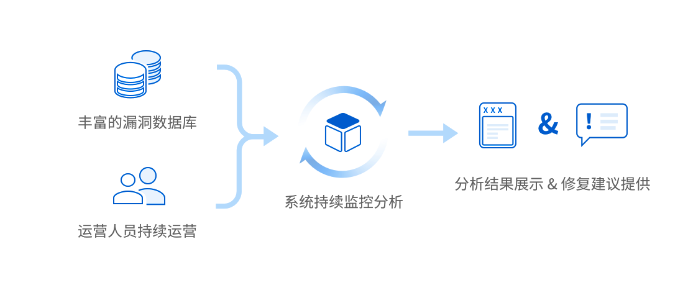
1、镜像检查能力已经覆盖到开发、测试等多个环节中,可快速发现镜像中存在的漏洞、病毒木马、Webshell等镜像风险。
2、可持续更新漏洞数据库,并与集群中的容器镜像进行匹配。一旦发现任何新镜像补丁信息,用户将收到通知,而不必定期重新扫描。
3、全方位检测镜像安全问题,5w+安全补丁库、四大应用组件漏洞、五大检测引擎,可深入发现镜像中的敏感信息。
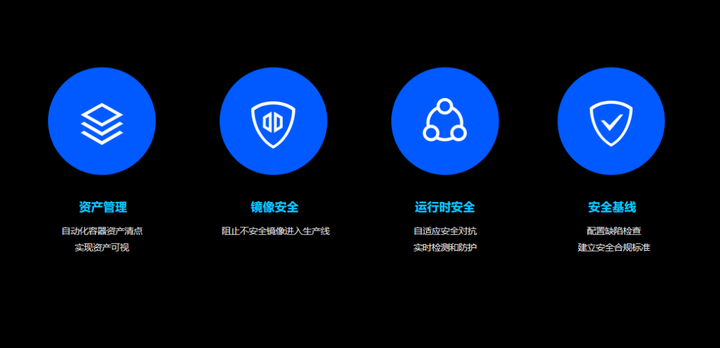
针对资产管理核查要求
1、容器资产种类全面盘点,支持容器、镜像、Registry、主机、POD等容器资产快速清点,为用户提供容器内资产的分类视图,实现容器资产的全面可视化。
2、容器资产内容深度识别,对每类资产进行深入分析,获取资产相关的高价值安全数据,帮助用户从安全角度细粒度观察资产运行状况。
3、自动化、持续性容器资产清点,系统资产数据持续更新,每日及时地、自动化上报资产数据。基于历史清点的数据,每次只清点新启动的进程信息,极大降低对服务器性能的耗损。

从日益新增的新型攻击威胁来看,云原生的安全将成为今后网络安全防护的关键。云原生安全领域面临的挑战和问题涉及容器安全、开发安全等多个方面,为了应对这些挑战和问题,我们需要采用有效的云原生安全方案,对提升企业安全防护能力是有很好的帮助,以确保云原生环境的安全性和稳定性。
